Smart Lighting ERC Researchers Demonstrate the First Monolithic Integration of an LED and High-Electron-Mobility Transistor on a Gallium Nitride Chip
June 5, 2013
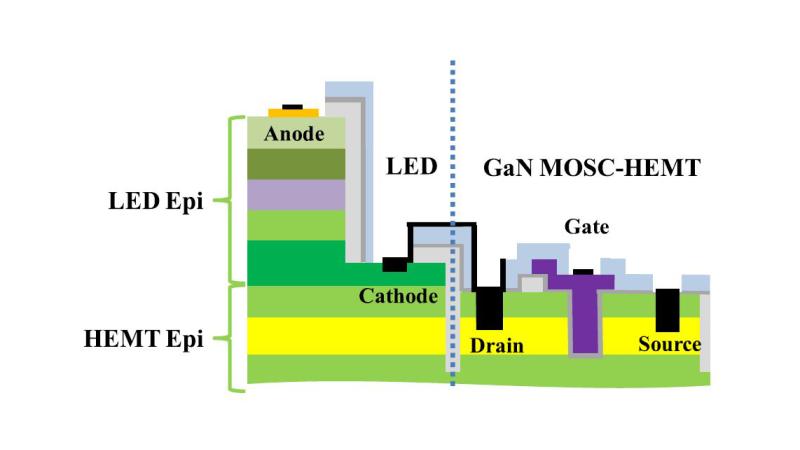
Researchers from the Smart Lighting Engineering Research Center at Rensselaer Polytechnic Institute have successfully integrated an LED and a power transistor on the same gallium nitride (GaN) chip. This innovation could open the door to a new generation of LED technology that is less expensive to manufacture, significantly more efficient, and which enables new functionalities and applications far beyond illumination.
At the heart of today’s LED (light-emitting diode) lighting systems are chips made from GaN, a semiconductor material. For the LED to function, many external components—such as inductors, capacitors, silicon interconnects, and wires—must be installed on or integrated into the chip. The large size of the chip, with all of these necessary components, complicates the design and performance of LED lighting products. Additionally, the process of assembling these complex LED lighting systems can be slow, manually intensive, and expensive.
In a new study led by T. Paul Chow, professor in the Department of Electrical, Computer, and Systems Engineering (ECSE) at Rensselaer, the researchers sought to solve this challenge by developing a chip with components all made from GaN. This type of monolithically integrated chip simplifies LED device manufacturing, with fewer assembly steps and less required automation. Additionally, LED devices made with monolithically integrated chips will have fewer parts to malfunction, higher energy efficiency and cost effectiveness, and greater lighting design flexibility.
Chow and the research team grew a GaN LED structure directly on top of a GaN high-electron-mobility transistor (HEMT) structure. They used several basic techniques to interconnect the two regions, creating what they are calling the first monolithic integration of a HEMT and an LED on the same GaN-based chip. The device, grown on a sapphire substrate, demonstrated light output and light density comparable to standard GaN LED devices. Chow said the study is an important step toward the creation of a new class of optoelectronic device called a light emitting integrated circuit (LEIC).
“Just as the integration of many silicon devices in a single chip—integrated circuits—has enabled powerful compact computers and a wide range of smart device technology, the LEIC will play a pivotal role in cost-effective monolithic integration of electronics and LED technology for new smart lighting applications and more efficient LED lighting systems,” Chow said.
“This new study, and the device we have created, is just the tip of the iceberg,” said Smart Lighting ERC Director Robert Karlicek, a co-author of the study and ECSE professor at Rensselaer. “LEICs will result in even higher energy efficiency of LED lighting systems. But what will be even more exciting are the new devices, new applications, and new breakthroughs enabled by LEICs—they will truly usher in the era of smart lighting.”
The study, titled “Monolithic integration of light-emitting diodes and power metal-oxide semiconductor channel high-electron-mobility transistors for light-emitting power integrated circuits in GaN on sapphire substrate,” was published recently in the journal Applied Physics Letters. See the study at: http://dx.doi.org/10.1063/1.4807125
Along with Chow and Karlicek, co-authors of the paper are: Christian Wetzel, the Wellfleet Constellation Professor of Future Chips at Rensselaer and a faculty member in the Department of Physics, Applied Physics, and Astronomy; Rensselaer graduate students Zhongda Li and John Waldron; and former Rensselaer research associate professor Theeradetch Detchprohm.
This research was funded by the National Science Foundation through the Smart Lighting ERC, with additional support from New York state though Empire State Development’s Division of Science, Technology and Innovation (NYSTAR).
The Smart Lighting ERC is primarily funded by the NSF. Since opening in 2008, the ERC has enlisted more than 25 key industrial partners to help guide the center’s research programs and hasten the transition from product idea to testing and commercialization. The center has a strong focus on the integration of LEDs and advanced control technology for the design of smart lighting systems. Along with being highly energy efficient and producing higher quality light, these smarter, feature-rich systems are poised to enable entirely new applications in areas as diverse as communications, health care, and biohazard sensing.
For additional information on the Smart Lighting ERC, visit:
- Center Homepage
http://smartlighting.rpi.edu/
- Rensselaer Moving Smarter Lighting Systems from the Laboratory to the Marketplace
http://news.rpi.edu/update.do?artcenterkey=3142
- Students Drive Effort To Introduce “Smart Lighting” on Rensselaer Campus
http://news.rpi.edu/update.do?artcenterkey=3117