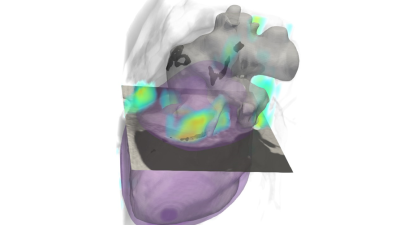
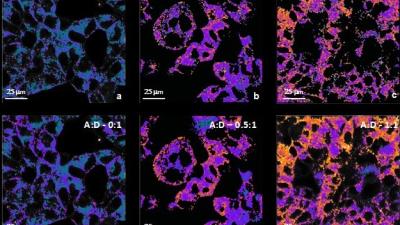
Pingkun Yan Named Head of RPI’s Department of Biomedical Engineering
Rensselaer Polytechnic Institute (RPI) has appointed Pingkun Yan, Ph.D., the P.K. Lashmet Career Development Chair Associate Professor at the Department of Biomedical Engineering at RPI, as head of the Department of Biomedical Engineering.